نیارش گستر ایران
ساختن دست یافتنی است!نیارش گستر ایران
ساختن دست یافتنی است!قدرت زلزله بر اساس ریشتر - Intensity of an Earthquake based on Richter Scales
زیر 2 ریشتر: غیر قابل احساس توسط انسان/ تنها توسط دستگاه ثبت می شود/ میلیون ها بار در سال در کره زمین می آید و امری مستمر است.
2 تا 3 ریشتر:
اکثر انسان ها
قادر به احساس آن نیستند و فقط اشیاء معلق، تکان مختصری می خورند./ سالانه
300 هزار زلزله 2 الی 3 ریشتری در کره زمین رخ می دهد.
3 تا 4 ریشتر:
وقتی در خانه اید احساس می کنید یک کامیون سنگین از پشت دیوار خانه رد می شود/ سالانه 49 هزار بار در کل جهان می آید.
4 تا 5 ریشتر:
اکثر مردم آن را
احساس می کنند، اشیاء داخل ساختمان به لرزش در می آیند، در و پنجره ها باز
و بسته می شوند؛ معمولا تلفات ندارد مگر افرادی که دچار وحشت شده اند یا
حین فرار آسیب می بینند/ 6300 بار در سال رخ می دهد.
5 تا 6 ریشتر:
همه مردم آن را
احساس می کنند، کمدها و اشیاء سنگین داخل خانه تکان می خورند، کنترل خودرو
حین رانندگی سخت می شود، خانه های سست فرو می ریزند و عده ای زیر آوار می
مانند./ در جهان سالانه 800 بار رخ می دهد.
6 تا 7 ریشتر:
ساختمان هایی که
در برابر زلزله مقاوم نیستند فرو می ریزند، برخی ساختمان های مقاوم نیز
دچار آسیب هایی می شوند و تلفات انسانی به بار می آید.
اغلب ساختمان ها فرو می ریزند، حتی ساختمان های موسوم به ضد زلزله هم خسارت هایی را متحمل می شوند، تلفات انسانی گسترده است و به دلیل فروریختن آوار در معابر، امداد رسانی مشکل خواهد بود.سیستم های خدمات شهری مانند لوله کشی آب و گاز و نیز برق قطع می شود و حتی امکان دارد آتش سوزی هم رخ دهد./ سالانه حدود 18 زلزله 7 تا 8 ریشتری در جهان رخ می دهد.
8 تا 10 ریشتر:
تخریب کامل، کشتار وسیع و تغییر شکل دائمی زمین در محل وقوع/ اگر کانون زمین لرزه در دریا و اقیانوس باشد، سونامی شکل می گیرد و شهرهای ساحلی اطراف را منهدم می کند/ به ندرت اتفاق می افتد
زلزله 10 ریشتری:
تا کنون ثبت نشده است ولی دانشمندان ژاپنی می گویند وقوع آن در 10 هزار سال آینده محتمل است که اگر بیاید، کل زمین یک ساعت خواهد لرزید و بخش اعظم خشکی ها زیر آب می روند و کاملاً نابود می شوند.
توجه داشته باشید که هر یک واحد که زلزله قوی تر می شود، قدرت تخریب آن به طور تصاعدی بالا می رود (که تا 31 برابر هم گفته اند). به همین دلیل است که زلزله 2 ریشتری قدرتی کمتر از انفجار 45 کیلوگرم تی ان تی دارد ولی زلزله 7 تا 8 ریشتری، معادل انفجار 100 بمب هیدروژنی انرژی آزاد می کند.

درباره قدرت زلزله بر اساس ریشتر چه می دانید؟
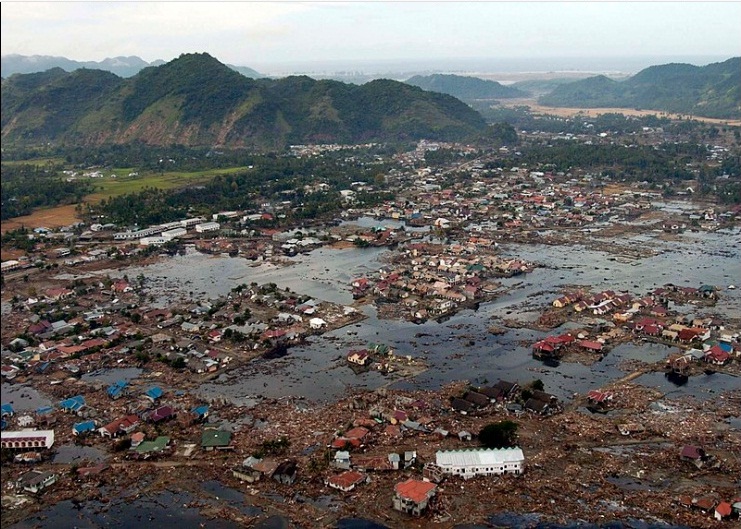
زمینلرزه و سونامی ۲۰۰۴ اقیانوس هند - 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami
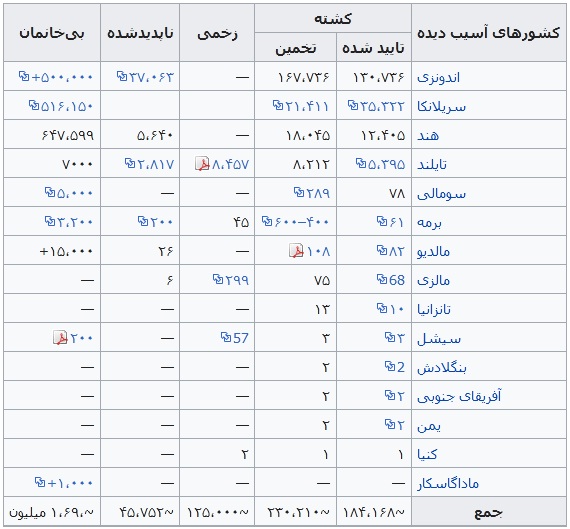
زلزلهٔ بزرگ اندونزی در مورخه ۲۶ دسامبر ۲۰۰۴ میلادی مطابق با ۶ دی ماه ۱۳۸۳ با بزرگای گشتاوری ۹/۱ ریشتر در عمق ۳۰ کیلومتری زمین و در فاصله ۱۶۰ کیلومتری شمال غرب سواحل سوماترای اندونزی درون اقیانوس هند اتفاق افتاد. این زمین لرزه سومین زلزله قدرتمند ثبت شده تاریخ و طولانیترین زمین لرزه نام گرفت که به مدت ده دقیقه مناطق اطراف را به لرزه درآورد. آبلرزه حاصل از این زلزله باعث مرگ بیش از ۲۸۶۰۰۰ نفر در ۱۴ کشور گوناگون شد. یکی از مناطقی که با وجود فاصله زیاد از مرکز لرزه آسیبهای جدی دیده بندر بیلا میباشد.
کشورهای آسیب دیده
Earthquake

